Latest News
Knee and Shoulder Joints Osteoarthitis
If you're suffering from knee pain, you're not alone. Almost one in three older than age 45 reports some type of knee pain, and it's a common reason that people visit their doctors or the emergency room.
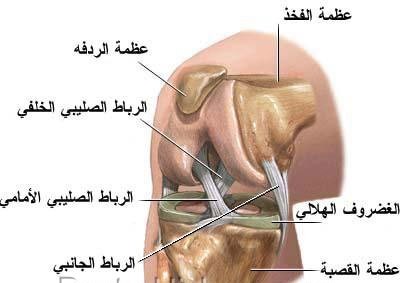
Knee Sprain
A knee sprain occurs when one or more ligaments in your knee are suddenly stretched or torn. Ligaments are tissues that hold bones together. Ligaments support the knee and keep the joint and bones lined up. They help you to be able to walk, twist and turn. There are four ligaments that help support the knee Ligaments are often sprained because of an exercise or sports-related injury. Treatment and recovery time depend on the type and cause of the knee sprain.
Osteoarthritis
It is a joint disease that causes the cushion layer between one's bones, or cartilage to wear away. It is also called degenerative joint disease. Symptoms are pain, tenderness in the knee, stiffness when standing or walking, loss of flexibility, and grating sensations that can be heard when the knee joint is used.
Osteoarthritis in the knee begins with the gradual deterioration of cartilage. Without the protective cartilage, the bones begin to rub together, causing pain, loss of mobility, and deformity. It affects approximately 16 million people. The majority of arthritis cases involving the knee are osteoarthritic cases.
Causes
It is not always certain why arthritis of the knee develops. Most physicians believe that it is a combination of factors that can include muscle weakness, obesity, heredity, joint injury or stress, constant exposure to the cold, and aging. Cartilage in the knee begins to break down and leaves the bones of the knee rubbing against each other as you walk. Persons who work in a place that applies repetitive stress on the knees are at a high risk of developing this condition.
Treatment using Minimally Invasive Techniques:
- Pulsed Radiofrequency:
PRF applied to the four branches of genicular nerves network supplying the knee joint, appear to provide a pain relief effect. Under fluoroscopic guidance four RF cannula are advanced percutaneous at ; medial aspect of Tibia , superior to fibula , superiomedial & superiolateral to epicondyle.
- Intra-articular LASER Weber Technology:
Successful pain reduction and sustainable regeneration of joint disorders. Weber Medicals new technique, percutaneous interstitial laser therapy (with the use of a sterile catheter) or intra-articular treatment, allows the laser light to successfully treat damaged joints, which can be irradiated directly and internally, resulting in significantly improved therapeutic results. With this technique we can reach depths of up to 12 inches. Green and blue lasers are normally absorbed by the surface of the tissue, thus the beneficial biological effects would not be used for joint issues, but using the interstitial laser technology, we can, for the first time bring blue and green laser to the inside of joints causing an anti-inflammatory effect.
.png)






